Take 3 minutes to read this article
Here at CentricsIT, we are your IT experts. When any IT maintenance issue arises in your data center, we are here to help. If there is an error code you can’t fix, let us assist you in our FixIT column. This post focuses on how to change Data Execution Prevention settings.
Understanding Data Execution Prevention
Data Execution Prevention (DEP) is a security feature that helps prevent damage from viruses and other security threats by monitoring your programs to make sure they use the computer’s memory safely.
If you want to turn off DEP for a program you trust, first check to see if the software publisher has made a DEP-compatible version of the program or made an update available before you change any DEP settings. If an update or DEP-compatible version is available, we recommend installing it and leaving DEP turned on so you can benefit from the protection it can provide. But if the publisher has not released an updated, DEP-compatible version of the program, you can turn off DEP for the program. When you make this change to Data Execution Prevention settings, you’ll be able to use the program, but it might be vulnerable to an attack that could spread to your other programs and files.
How to Change Data Execution Prevention Settings
Instructions for Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2012
- Click the Startbutton, right-clicking Computer, and then clicking Properties.
- ClickAdvanced system settings. If you’re prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
- UnderPerformance, click Settings.
- Click theData Execution Prevention tab, and then click Turn on DEP for all programs and services except those I select.
- To turn off DEP for an individual program, select the check box next to the program that you want to turn off DEP for, and then clickOK.
If the program is not in the list, click Add. Browse to the Program Files folder, find the executable file for the program (it will have an .exe file name extension), and then click Open.
- ClickOK, click OK in the System Properties dialog box if it appears, and then click OK You might need to restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Instructions for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003
- Click Start, right-click My Computer, and then click Properties.
- Click the Advanced tab, and then click Settings under the Startup and Recovery
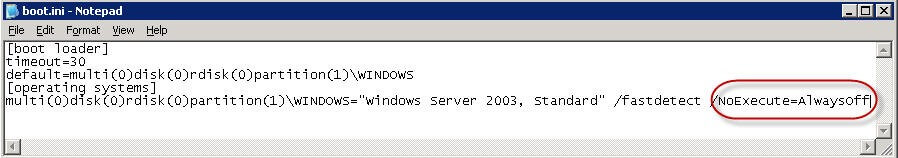
- In the System Startup field, click Edit. The Boot.ini file opens in Notepad.
- In Notepad, click Find on the Edit menu.
- In the Find what box, type /noexecute, and then click Find Next.
- In the Find dialog box, click Cancel.
- Replace policy level after /noexecute= with the value you desire. The default value is OptIn.
- OptIn -This setting is the default configuration. On systems with processors that can implement hardware-enforced DEP, DEP is enabled by default for limited system binaries and programs that “opt-in.” With this option, only Windows system binaries are covered by DEP by default.
- OptOut -DEP is enabled by default for all processes. You can manually create a list of specific programs that do not have DEP applied by using the System dialog box in Control Panel. Information technology (IT) professionals can use the Application Compatibility Toolkit to “opt-out” one or more programs from DEP protection. System compatibility fixes, or shims, for DEP do take effect.
- Alwayson -This setting provides full DEP coverage for the whole system. All processes always run with DEP applied. The exceptions list to exempt specific programs from DEP protection is not available. System compatibility fixes for DEP do not take effect. Programs that have been opted-out by using the Application Compatibility Toolkit run with DEP applied.
- Alwaysoff -This setting does not provide any DEP coverage for any part of the system, regardless of hardware DEP support. The processor does not run in PAE mode unless the /PAE option is present in the Boot.ini file.
- Click File then Save
- Restart Windows to put into effect the change in Data Execution Prevention Settings.





